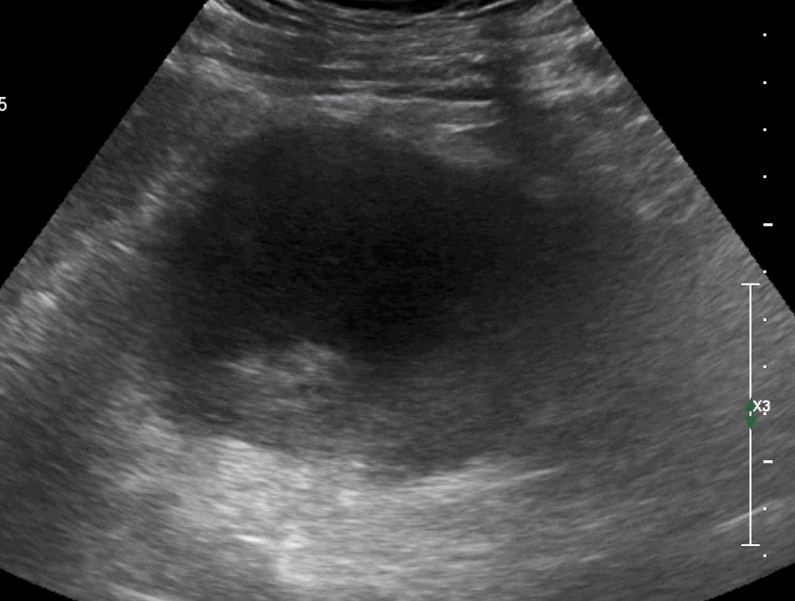
General information
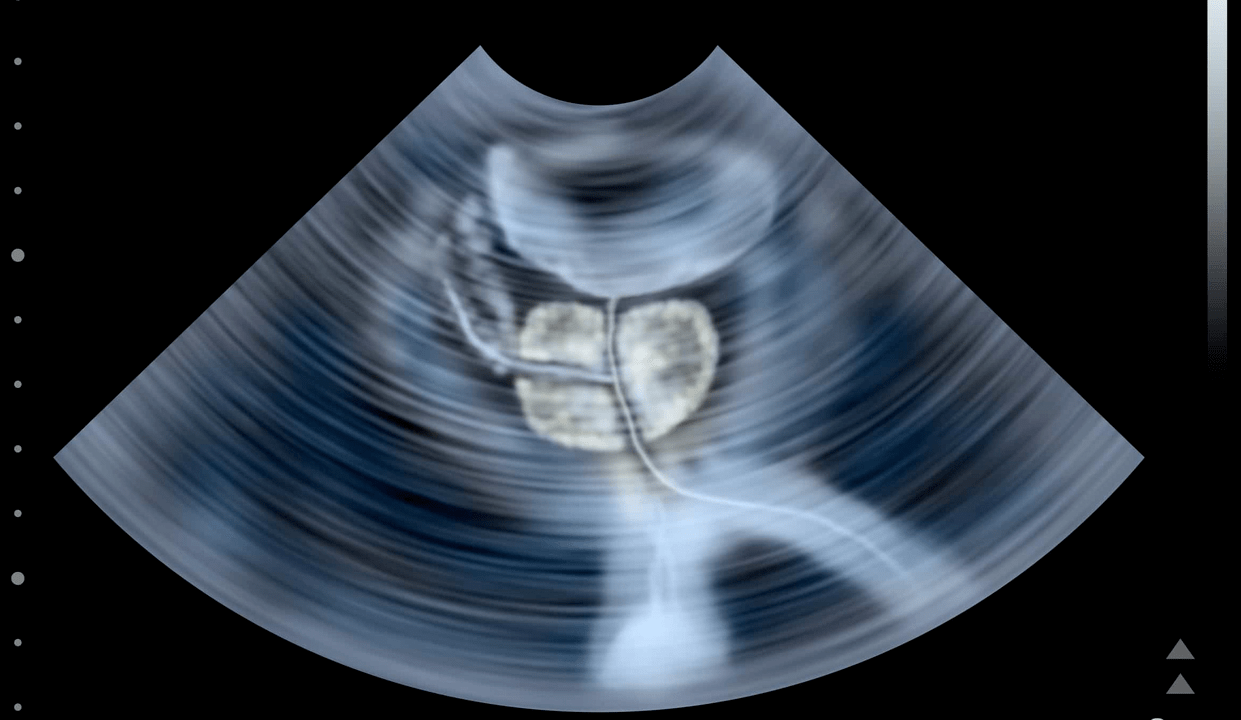
Causes of calculus prostatitis
Symptoms of calculus prostatitis
Diagnosis of calculus prostatitis
Treatment of calculus prostatitis

Treatment of calculus prostatitis
the cause of this disease
- Urinary tract injury;
- Weakness of the prostate and seminal tubercle;
- Previous surgeries and invasive procedures.
- Small pelvic varicose veins;
- Metabolic disorders caused by systemic pathology;
- An inactive lifestyle can lead to the development of pelvic organ stagnation;
- Irregular sex life;
- Alcoholism, smoking;
- uncontrolled use of certain drugs;
- Damage to the prostate during surgery and long-term catheterization.
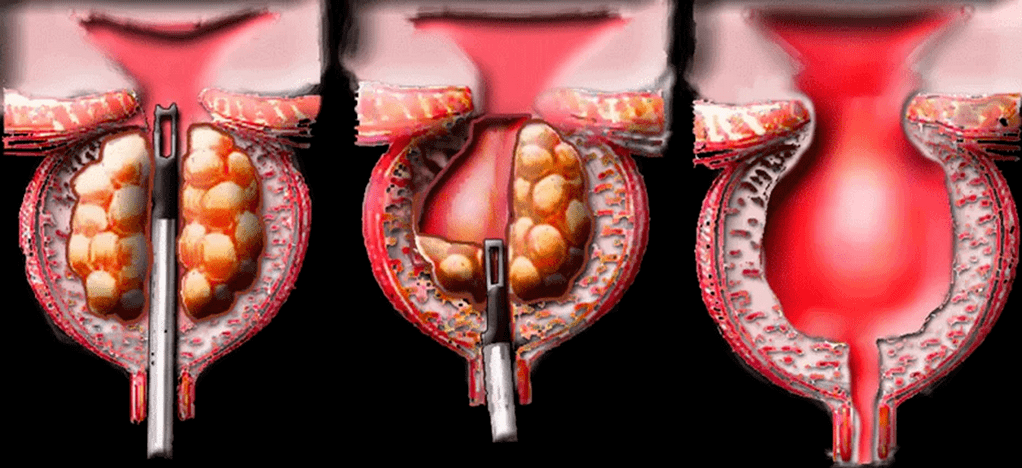
Types of stones in calculus prostatitis
- real. They form directly in the acini and ducts.
- Incorrect. They migrate from the upper urinary tract (kidneys, bladder, urethra) to the prostate.
disease symptoms
- Frequent urination or complete urinary retention;
- Hematuria and presence of blood inclusions in semen;
- Prostatic leakage – leakage of secretions from the prostate;
- Decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, painful ejaculation;
- Nervous system disorders: irritability, increased fatigue, insomnia.
- Atrophy and hardening of glandular tissue;
- Prostate abscess.
diagnosis
laboratory diagnosis
- Culture of prostate secretions. Importantly informative method for identifying pathogenic microorganisms and diagnosing prostatic inflammatory processes.
- Urine culture. Allows you to detect pathogenic infections in urine and determine their type and concentration. If prostatic inflammation is suspected, a culture is obtained to confirm the diagnosis.
- PCR studies of scrapings. Allows you to detect sexually transmitted infections and identify pathogens.
- PSA analysis. Allows you to rule out prostate cancer, which usually occurs against the background of prostatitis.
- General clinical analysis of blood and urine. It is used to identify hidden inflammatory processes and kidney diseases in the urinary tract.
- Sperm diagram. Ejaculations are analyzed to rule out or confirm infertility.
Instrument diagnostics
Treatment of calculus prostatitis
Conservative treatment
- antibiotic. Eliminate infection and stop inflammation. Drug type, dose, and course duration were determined individually for each patient.
- NSAIDs. They block the inflammatory process and help eliminate pathological symptoms: pain, swelling.
- Antispasmodics. Relieve muscle spasms and reduce pain.
- Alpha adrenergic blockers. Facilitates the urination process.
- Vitamin mineral complex, immune modulator. Strengthens the immune system and promotes speedy recovery.
- Eliminate stalled processes;
- Activates tissue regeneration.
- The most effective physical therapy method for treating calculus prostatitis:
- Ultrasound therapy, shock wave therapy.
Surgery
chronic calculus prostatitis

- Chronic Sexually Transmitted Infections (STDs)
- Prolonged infection process, inflammation of prostate ducts and tissues;
- Prostate congestion, which is mainly related to irregular sexual life in men;
- Urethroprostatic reflux - pathological reflux of small amounts of urine into the prostate;
- Genetic predisposition – A relative has calculus prostatitis.
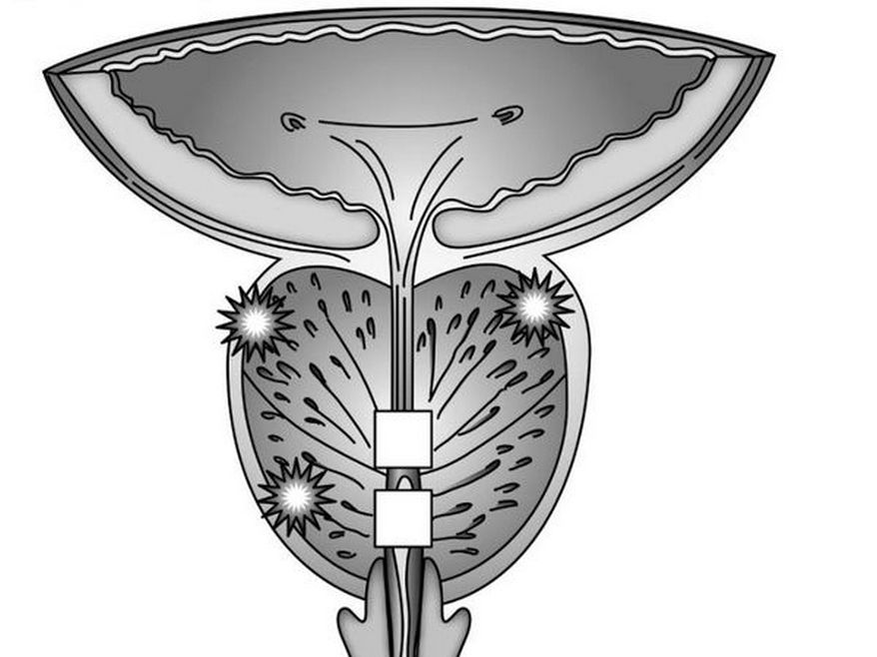
Symptoms of calculus prostatitis
- erectile dysfunction;
- Pain in the groin area, which may be spasmodic and paroxysmal in nature;
- During ejaculation – indicates damage to the prostatic canaliculi and blood vessels by the sharp edges of the stones;
- Premature ejaculation and painful ejaculation.


This method is very dangerous because it can exacerbate the pathological process and lead to the development of complications.
The treatment of calculus prostatitis is complex
- antibiotic,
- anti-inflammatory drugs,
- enzyme
- immune drugs
- Phytotherapy,
- Physical therapy procedures.